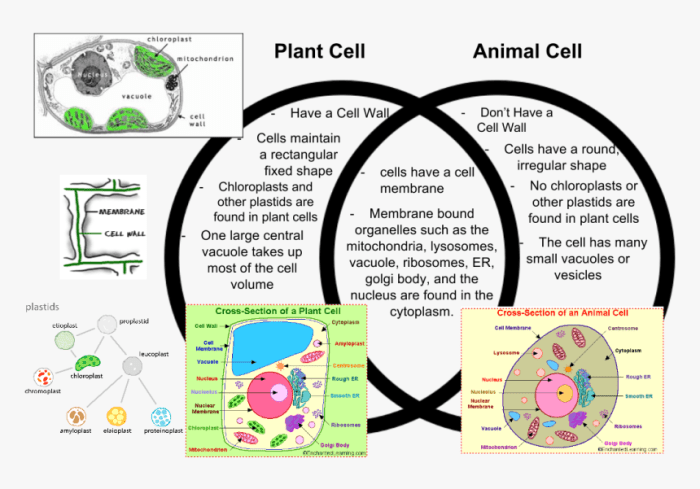
Plant cells vs animal cells venn diagram – In the realm of biology, the distinction between plant and animal cells holds profound significance. This comprehensive analysis, presented through an illuminating Venn diagram, unveils the intricate similarities and striking differences between these fundamental units of life, offering a deeper understanding of their unique adaptations and vital roles in the tapestry of nature.
Cell Structures
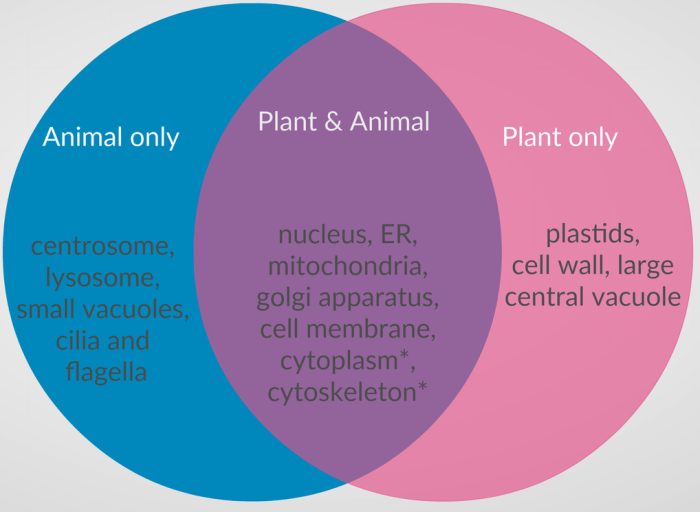
Plant and animal cells share many common structures, including a cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and various organelles. These structures perform essential functions necessary for cell survival and function.
Structures Unique to Plant Cells
- Cell Wall:A rigid structure made of cellulose that provides support and protection.
- Chloroplasts:Organelles containing chlorophyll that carry out photosynthesis, converting sunlight into energy.
- Vacuole:A large, fluid-filled sac that stores water, nutrients, and waste products.
Cell Walls and Membranes: Plant Cells Vs Animal Cells Venn Diagram
Differences Between Cell Walls and Cell Membranes
- Composition:Cell walls are made of cellulose, while cell membranes are made of phospholipids and proteins.
- Location:Cell walls are located outside the cell membrane in plant cells, while cell membranes are the outermost layer of all cells.
- Function:Cell walls provide structural support and protection, while cell membranes regulate the movement of substances into and out of the cell.
Composition and Functions of Cell Walls
Cell walls in plant cells are primarily composed of cellulose, a strong and rigid material that provides structural support. They also contain other molecules, such as hemicellulose and pectin, which contribute to the wall’s strength and flexibility.
Role of Cell Membranes
Cell membranes play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the cell and regulating the exchange of substances. They control the passage of molecules into and out of the cell, maintaining a stable internal environment.
Organelles
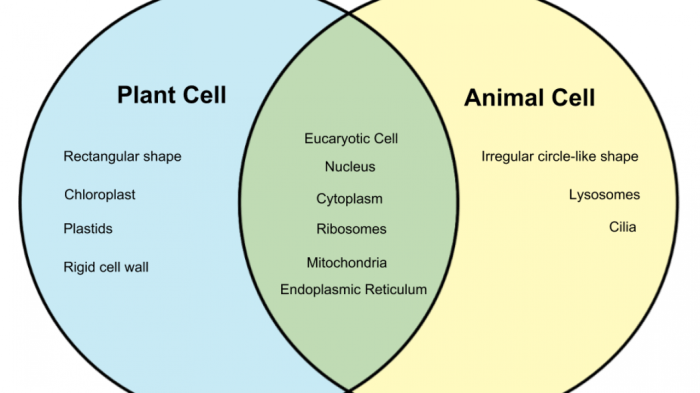
Table of Organelles, Plant cells vs animal cells venn diagram
| Organelle | Present in Both | Unique to Plant Cells | Unique to Animal Cells |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Membrane | Yes | No | No |
| Cytoplasm | Yes | No | No |
| Nucleus | Yes | No | No |
| Mitochondria | Yes | No | No |
| Ribosomes | Yes | No | No |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | Yes | No | No |
| Golgi Apparatus | Yes | No | No |
| Lysosomes | No | No | Yes |
| Centrosomes | No | No | Yes |
| Chloroplasts | No | Yes | No |
| Vacuole | No | Yes | No |
Cell Division
Process of Cell Division
Cell division is the process by which cells reproduce, creating new cells to replace old ones or to facilitate growth and development. In both plant and animal cells, cell division involves two main phases: mitosis and cytokinesis.
Similarities and Differences Between Mitosis and Meiosis
- Mitosis:Occurs in somatic cells (non-reproductive cells) and produces two genetically identical daughter cells.
- Meiosis:Occurs in reproductive cells (gametes) and produces four genetically distinct daughter cells.
Flowchart of Cell Division
- Interphase:The cell prepares for division by replicating its DNA.
- Prophase:The chromosomes condense and become visible.
- Metaphase:The chromosomes align in the center of the cell.
- Anaphase:The chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase:Two new nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes, and cytokinesis begins.
- Cytokinesis:The cytoplasm divides, creating two separate daughter cells.
Energy Production
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants and other photosynthetic organisms convert sunlight into chemical energy stored in the form of glucose. This process occurs in chloroplasts and requires the presence of chlorophyll, a green pigment that absorbs sunlight.
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert glucose into energy that can be used to power cellular activities. This process occurs in mitochondria and involves a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose and release energy.
Role of Chloroplasts and Mitochondria
Chloroplasts and mitochondria are essential organelles for energy production in plant and animal cells, respectively. Chloroplasts capture sunlight and convert it into glucose through photosynthesis, while mitochondria break down glucose and release energy through cellular respiration.
Cell Function
Functions of Plant and Animal Cells
Plant and animal cells perform specialized functions that contribute to the overall functioning of multicellular organisms.
Specialized Structures and Organelles
The specialized structures and organelles found in plant and animal cells enable them to perform their specific functions. For example, the cell wall in plant cells provides support and protection, while the lysosomes in animal cells aid in digestion.
Examples of Cell Functions
- Plant Cells:Photosynthesis, storage of nutrients, production of oxygen
- Animal Cells:Digestion, muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission
FAQ Compilation
What is the primary difference between plant and animal cells?
Plant cells possess a rigid cell wall, chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and a large central vacuole, while animal cells lack these features.
How do plant and animal cells obtain energy?
Plant cells utilize sunlight through photosynthesis, while animal cells rely on cellular respiration to generate energy.
What is the role of organelles in cell function?
Organelles are specialized structures within cells that perform specific tasks, such as protein synthesis, energy production, and waste removal.