Which of the following statements is true about double-stranded DNA? This question delves into the fundamental structure and characteristics of double-stranded DNA, a molecule that serves as the blueprint for life and plays a pivotal role in various biological processes.
Double-stranded DNA is a complex and fascinating molecule with a unique structure that enables it to store and transmit genetic information. Understanding the properties and functions of double-stranded DNA is crucial for comprehending the mechanisms of inheritance, gene expression, and the development of novel therapeutic approaches.
Structure of Double-Stranded DNA: Which Of The Following Statements Is True About Double-stranded Dna
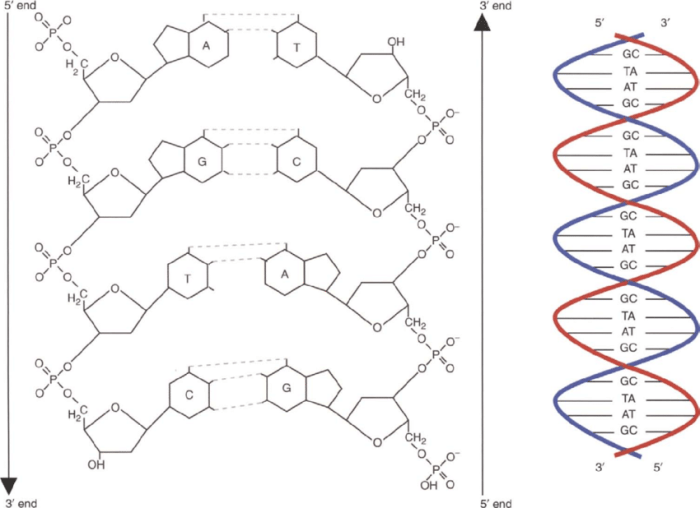
Double-stranded DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a molecule that contains the genetic instructions for an organism. It is composed of two polynucleotide chains that are twisted around each other to form a double helix. Each chain is made up of a series of nucleotides, which are composed of a nitrogenous base, a sugar molecule, and a phosphate group.
Two Polynucleotide Chains
The two polynucleotide chains in double-stranded DNA are antiparallel, meaning that they run in opposite directions. The bases on one chain are complementary to the bases on the other chain, meaning that adenine (A) on one chain always pairs with thymine (T) on the other chain, and cytosine (C) on one chain always pairs with guanine (G) on the other chain.
Hydrogen Bonds
The complementary bases are held together by hydrogen bonds. These bonds form between the amino group of adenine and the keto group of thymine, and between the amino group of cytosine and the keto group of guanine.
Double Helix Structure
The two polynucleotide chains are twisted around each other to form a double helix. The double helix has a major groove and a minor groove. The major groove is wider and shallower than the minor groove, and it is where proteins that interact with DNA can bind.
Replication of Double-Stranded DNA
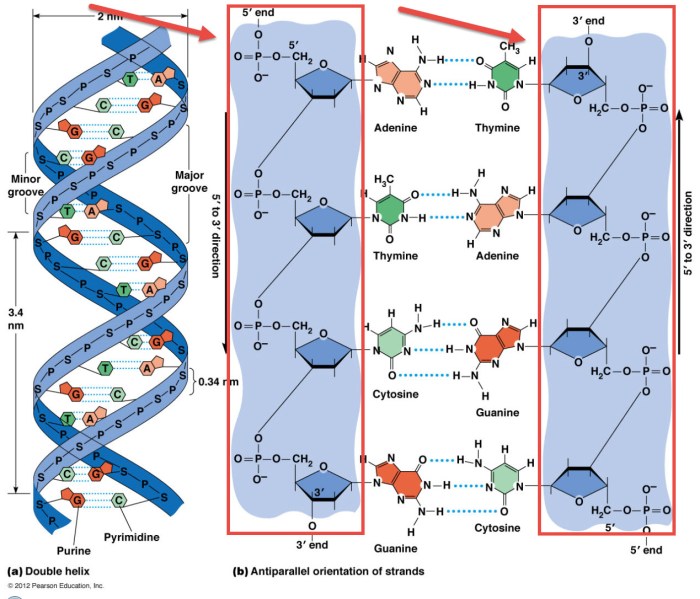
Double-stranded DNA is replicated during cell division. The process of DNA replication is carried out by an enzyme called DNA polymerase. DNA polymerase unwinds the double helix and separates the two strands. It then uses the complementary bases on each strand to synthesize new strands of DNA.
Role of DNA Polymerase, Which of the following statements is true about double-stranded dna
DNA polymerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the polymerization of deoxyribonucleotides into a DNA strand. It requires a template strand to guide the synthesis of the new strand.
Unwinding and Separation of Strands
The double helix is unwound by an enzyme called helicase. Helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between the complementary bases, allowing the two strands to separate.
Synthesis of New DNA Strands
DNA polymerase synthesizes new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the 3′ end of the growing strand. The nucleotides are added in a complementary fashion, meaning that adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine.
Function of Double-Stranded DNA
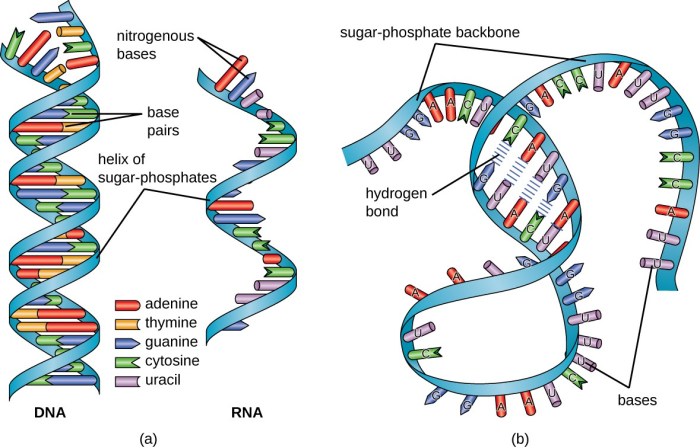
Double-stranded DNA is the genetic material of all living organisms. It contains the instructions for the development and functioning of the organism.
Storage of Genetic Information
The genetic information in double-stranded DNA is stored in the sequence of nucleotides. The sequence of nucleotides determines the amino acid sequence of proteins, which in turn determines the structure and function of the protein.
Role in Protein Synthesis
Double-stranded DNA is transcribed into RNA, which is then translated into protein. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in the protein.
Comparison to Single-Stranded DNA
Single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) is a molecule that contains only one polynucleotide chain. It is found in some viruses and in some bacteria.
Structure
ssDNA is less stable than double-stranded DNA because it lacks the hydrogen bonds that hold the two strands together. ssDNA is also more flexible than double-stranded DNA.
Roles
ssDNA plays a variety of roles in biological systems. It is used as a template for DNA replication and transcription, and it is also involved in some DNA repair processes.
Applications of Double-Stranded DNA
Double-stranded DNA is used in a variety of applications in genetic engineering and biotechnology.
Genetic Engineering
Double-stranded DNA can be used to create genetically modified organisms (GMOs). GMOs are organisms whose DNA has been altered in a way that does not occur naturally.
DNA Fingerprinting
DNA fingerprinting is a technique that is used to identify individuals. It is based on the fact that each individual has a unique DNA sequence.
DNA Sequencing
DNA sequencing is a technique that is used to determine the sequence of nucleotides in a DNA molecule. DNA sequencing is used in a variety of applications, including medical diagnosis and forensic science.
FAQ Guide
What is the difference between double-stranded DNA and single-stranded DNA?
Double-stranded DNA consists of two polynucleotide chains that run antiparallel to each other and are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary bases. Single-stranded DNA, on the other hand, consists of a single polynucleotide chain and lacks the complementary strand.
What is the role of double-stranded DNA in protein synthesis?
Double-stranded DNA serves as the template for RNA synthesis during transcription. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA is transcribed into a complementary RNA molecule, which then serves as the template for protein synthesis during translation.
How is double-stranded DNA replicated?
Double-stranded DNA is replicated during cell division through a process called DNA replication. During replication, the double helix unwinds, and each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand.