Label each element involved in bacterial transcription in the figure. – Labeling the elements involved in bacterial transcription is a crucial step in understanding the fundamental processes of gene expression. This comprehensive guide will provide a clear and concise overview of each element, its role, and its interaction with RNA polymerase.
The promoter region, RNA polymerase, transcription initiation, elongation, and termination are the key elements that drive bacterial transcription. Each of these elements plays a specific role in the synthesis of RNA molecules from DNA templates.
Bacterial Transcription: Label Each Element Involved In Bacterial Transcription In The Figure.
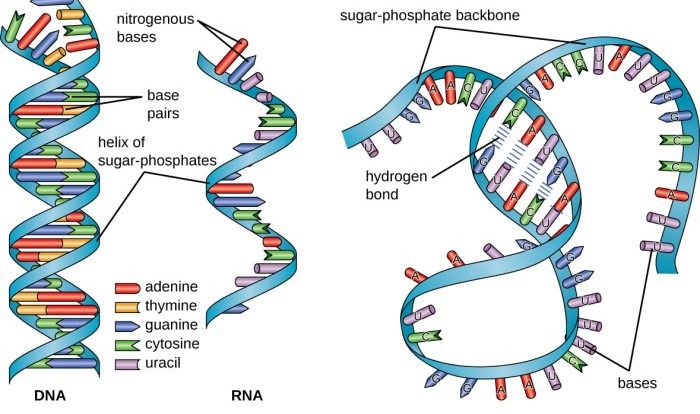
Bacterial transcription is the process by which the genetic information encoded in DNA is used to synthesize RNA molecules. RNA molecules are essential for protein synthesis, which is the process by which cells make the proteins they need to function.
Promoter Region
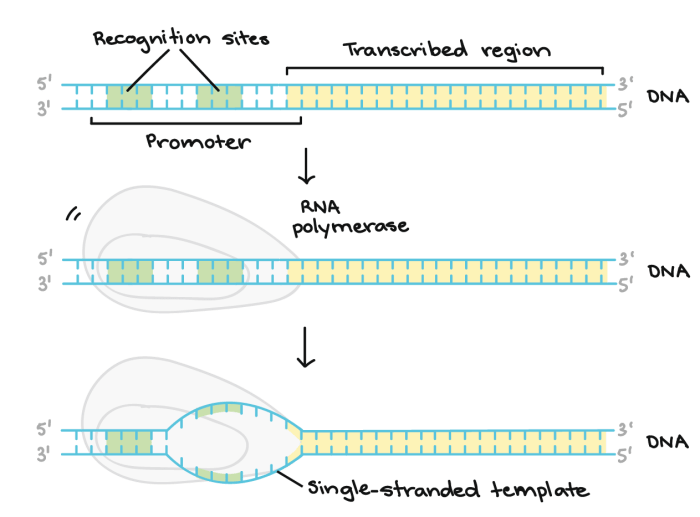
The promoter region is a region of DNA that is located upstream of the transcription start site. The promoter region contains the sequences that are recognized by RNA polymerase, the enzyme that synthesizes RNA molecules.
The promoter region is essential for transcription initiation. Without a promoter region, RNA polymerase would not be able to bind to the DNA and begin synthesizing an RNA molecule.
RNA Polymerase
RNA polymerase is a large, complex enzyme that is responsible for synthesizing RNA molecules. RNA polymerase is composed of several subunits, each of which has a specific function.
The core subunits of RNA polymerase are responsible for binding to the promoter region and synthesizing the RNA molecule. The other subunits of RNA polymerase are responsible for regulating the activity of the core subunits.
Transcription Initiation, Label each element involved in bacterial transcription in the figure.
Transcription initiation is the process by which RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region and begins synthesizing an RNA molecule.
The first step in transcription initiation is the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter region. RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region through a series of interactions between the promoter region and the RNA polymerase subunits.
Once RNA polymerase is bound to the promoter region, it begins unwinding the DNA double helix. This allows RNA polymerase to access the template strand of DNA, which is the strand of DNA that is used to synthesize the RNA molecule.
RNA polymerase then begins synthesizing the RNA molecule by adding nucleotides to the growing RNA chain. Nucleotides are the building blocks of RNA molecules.
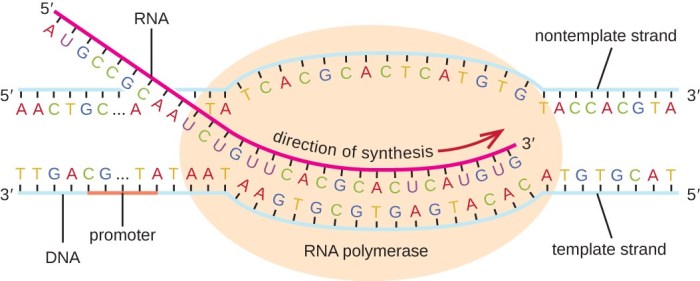
Elongation
Elongation is the process by which RNA polymerase moves along the DNA template and adds nucleotides to the growing RNA molecule.
RNA polymerase moves along the DNA template in a 5′ to 3′ direction. This means that RNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the 3′ end of the growing RNA molecule.
As RNA polymerase moves along the DNA template, it unwinds the DNA double helix. This allows RNA polymerase to access the template strand of DNA and add nucleotides to the growing RNA molecule.
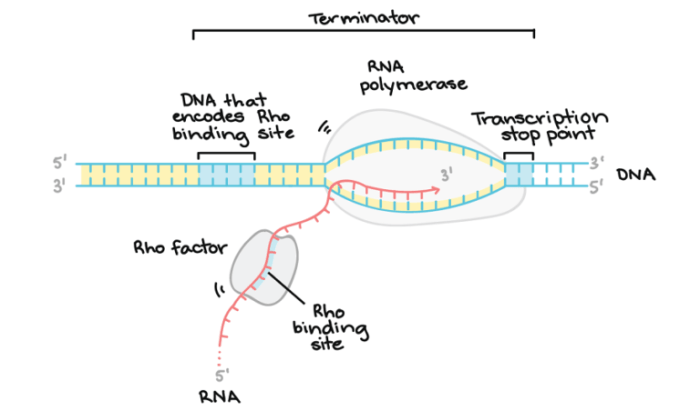
Termination
Termination is the process by which RNA polymerase releases the newly synthesized RNA molecule.
Termination occurs when RNA polymerase reaches a termination signal. Termination signals are sequences of DNA that signal RNA polymerase to stop synthesizing the RNA molecule.
Once RNA polymerase reaches a termination signal, it releases the newly synthesized RNA molecule and dissociates from the DNA template.
Popular Questions
What is the role of the promoter region in bacterial transcription?
The promoter region serves as the binding site for RNA polymerase, initiating the transcription process.
How does RNA polymerase recognize the promoter region?
RNA polymerase recognizes specific DNA sequences within the promoter region, known as consensus sequences, which are essential for transcription initiation.
What is the process of transcription elongation?
During elongation, RNA polymerase unwinds the DNA double helix and synthesizes a complementary RNA molecule by adding nucleotides to the growing RNA chain.