Introducing the gene regulation inquiry answer key, a comprehensive guide to unraveling the intricate mechanisms that govern gene expression. This definitive resource empowers researchers with a wealth of knowledge, providing clarity and understanding in the complex realm of gene regulation.
Delving into the intricacies of gene regulation, this guide explores the processes, methods, and applications that shape our understanding of gene expression. From the fundamental mechanisms to the cutting-edge research, this answer key serves as an invaluable tool for students, scientists, and professionals alike.
Gene Regulation Mechanisms: Gene Regulation Inquiry Answer Key
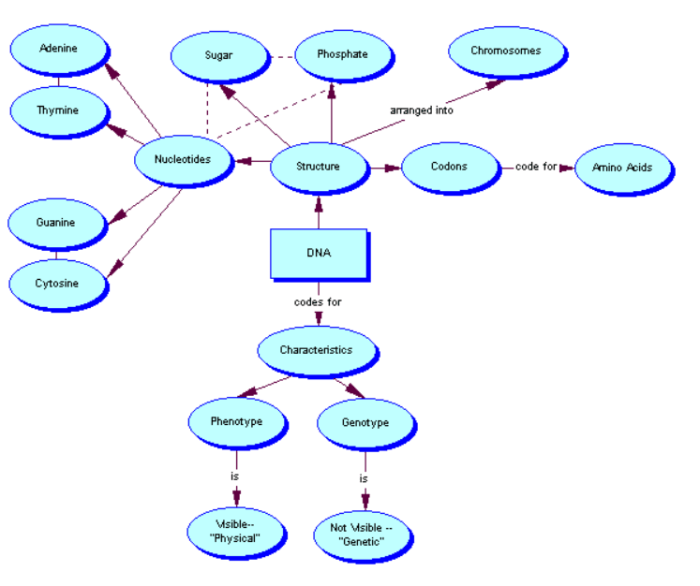
Gene regulation is a fundamental process in biology that controls the expression of genes, determining which genes are active and when. It plays a crucial role in development, differentiation, and homeostasis. Gene regulation involves a complex interplay of various mechanisms that modulate gene activity at different stages, including transcription, translation, and post-translational modifications.
Transcriptional Regulation
Transcriptional regulation is a key mechanism that controls the initiation and rate of transcription, the process by which DNA is transcribed into RNA. This regulation can occur at multiple stages:
-
-*Promoter Recognition
Transcription factors bind to specific DNA sequences called promoters, located upstream of genes, to initiate transcription.
-*Enhancer and Silencer Elements
Enhancers and silencers are DNA sequences that can bind transcription factors and influence the activity of promoters from a distance.
-*Chromatin Modifications
Modifications to chromatin, the complex of DNA and proteins, can alter gene accessibility and influence transcription.
Translational Regulation
Translational regulation involves the control of protein synthesis from mRNA. This regulation can occur through:
-
-*mRNA Stability
The stability and degradation of mRNA molecules can influence the amount of protein produced.
-*Translational Initiation
Translation initiation factors regulate the binding of ribosomes to mRNA and the start of translation.
-*Ribosomal Modifications
Chemical modifications to ribosomes can affect the efficiency of translation.
Post-Translational Modifications, Gene regulation inquiry answer key
Post-translational modifications (PTMs) are chemical changes to proteins that can alter their activity, localization, or stability. Common PTMs include phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and glycosylation.
Questions Often Asked
What is gene regulation?
Gene regulation refers to the processes that control the expression of genes, determining when and where specific genes are turned on or off.
How do transcription factors regulate gene expression?
Transcription factors bind to specific DNA sequences and either promote or repress the transcription of nearby genes, influencing gene expression.
What is the significance of gene regulation research?
Gene regulation research holds immense potential for medicine and biotechnology, enabling the development of new therapies and advancements in genetic engineering.