Compare mitosis and meiosis worksheet – Embarking on the exploration of mitosis and meiosis, this comprehensive worksheet delves into the fundamental processes that govern cell division. By comparing mitosis and meiosis, we unravel the intricate mechanisms underlying genetic inheritance and cellular reproduction.
Throughout this guide, we will meticulously examine the stages of each process, highlighting their similarities and differences. Moreover, we will explore the practical applications of mitosis and meiosis, shedding light on their significance in tissue repair, growth, and genetic diversity.
Overview of Mitosis and Meiosis
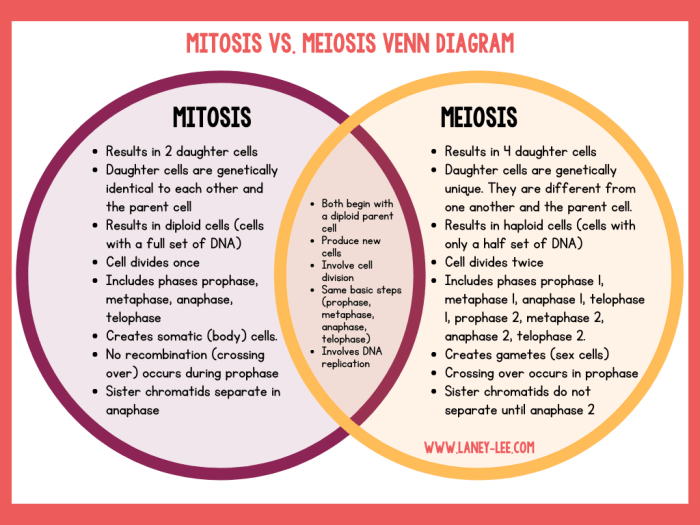
Mitosis and meiosis are two fundamental processes of cell division that occur in all living organisms. Mitosis is responsible for the growth and repair of tissues, while meiosis is responsible for the production of gametes (sex cells) and genetic diversity.
The key characteristics of mitosis and meiosis are summarized in the following table:
| Characteristic | Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Growth and repair | Production of gametes |
| Number of daughter cells | 2 | 4 |
| Chromosome number | Diploid (2n) | Haploid (n) |
| Cell division stages | Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase | Prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I, prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, telophase II |
Stages of Mitosis: Compare Mitosis And Meiosis Worksheet
Mitosis is a continuous process, but it can be divided into four distinct stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
- Prophase:During prophase, the chromosomes become visible and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase:During metaphase, the chromosomes line up in the center of the cell.
- Anaphase:During anaphase, the chromosomes are separated and pulled to opposite ends of the cell.
- Telophase:During telophase, two new nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes and the cell membrane pinches in the middle, dividing the cell into two daughter cells.
Stages of Meiosis

Meiosis is a more complex process than mitosis and consists of two rounds of cell division: meiosis I and meiosis II.
Meiosis I, Compare mitosis and meiosis worksheet
- Prophase I:During prophase I, the chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through a process called crossing over. The nuclear envelope then breaks down.
- Metaphase I:During metaphase I, the chromosomes line up in the center of the cell.
- Anaphase I:During anaphase I, the chromosomes are separated and pulled to opposite ends of the cell.
- Telophase I:During telophase I, two new nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes and the cell membrane pinches in the middle, dividing the cell into two daughter cells.
Meiosis II
- Prophase II:During prophase II, the chromosomes become visible again and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase II:During metaphase II, the chromosomes line up in the center of the cell.
- Anaphase II:During anaphase II, the chromosomes are separated and pulled to opposite ends of the cell.
- Telophase II:During telophase II, two new nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes and the cell membrane pinches in the middle, dividing the cell into two daughter cells.
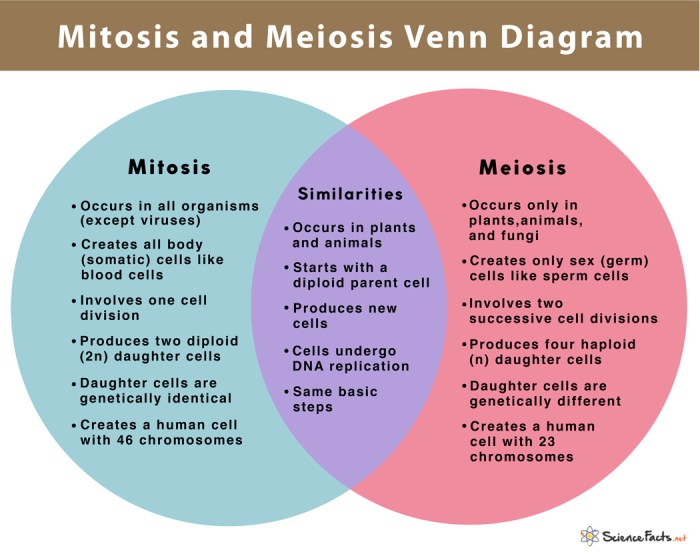
Comparison of Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis and meiosis are both essential processes for life, but they differ in several key ways.
- Purpose:Mitosis is responsible for growth and repair, while meiosis is responsible for the production of gametes and genetic diversity.
- Number of daughter cells:Mitosis produces two daughter cells, while meiosis produces four daughter cells.
- Chromosome number:Mitosis produces daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell, while meiosis produces daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
- Cell division stages:Mitosis consists of four stages (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase), while meiosis consists of two rounds of cell division (meiosis I and meiosis II), each with four stages.
Mitosis and meiosis both contribute to genetic variation. Mitosis contributes to genetic variation through the random distribution of chromosomes to daughter cells during cell division. Meiosis contributes to genetic variation through crossing over during prophase I and the random distribution of chromosomes to daughter cells during both rounds of cell division.
Mitosis occurs in all living organisms, while meiosis only occurs in sexually reproducing organisms.
Applications of Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis and meiosis have a wide range of practical applications.
Mitosisis used in tissue repair and growth. For example, mitosis is responsible for the healing of wounds and the growth of new tissue.
Meiosisis used in sexual reproduction and genetic diversity. Meiosis is responsible for the production of gametes (sex cells), which combine to form a zygote. The zygote then develops into a new organism. Meiosis also contributes to genetic diversity by shuffling the chromosomes during crossing over and the random distribution of chromosomes to daughter cells during both rounds of cell division.
Questions and Answers
What is the primary difference between mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis produces two genetically identical daughter cells, while meiosis produces four genetically distinct daughter cells.
How do the stages of mitosis differ from those of meiosis?
Mitosis consists of prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, while meiosis consists of meiosis I (prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I) and meiosis II (prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, telophase II).
What are the practical applications of mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis is essential for tissue repair and growth, while meiosis is crucial for sexual reproduction and genetic diversity.
