Which molecule listed below has a polar covalent bond? As we delve into this intriguing question, we embark on a journey through the captivating realm of molecular interactions, where the polarity of chemical bonds shapes the very nature of matter.
Prepare to be captivated as we unravel the secrets of bond polarity, exploring its profound influence on molecular properties and behavior.
In this comprehensive guide, we will dissect the concept of polar covalent bonds, uncovering the factors that govern their formation and exploring their far-reaching implications. Through detailed examples and engaging discussions, we will illuminate the intricacies of bond polarity, empowering you with a deeper understanding of the fundamental forces that drive molecular interactions.
Polar Covalent Bond Definition

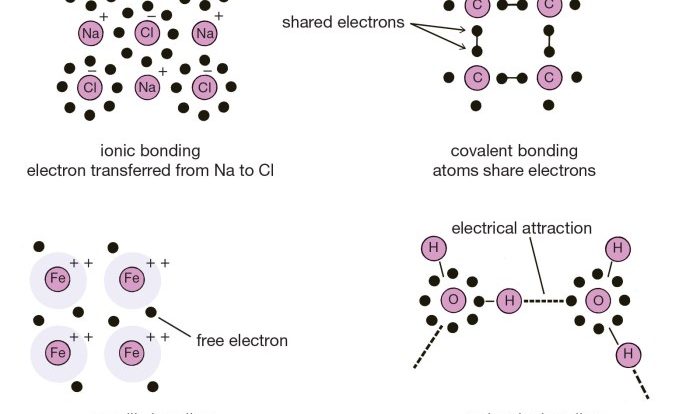
A polar covalent bond is a type of chemical bond in which the electrons are not shared equally between the two atoms. This results in a partial positive charge on one atom and a partial negative charge on the other.
Examples of molecules with polar covalent bonds include:
- Water (H 2O)
- Ammonia (NH 3)
- Hydrogen chloride (HCl)
Factors Influencing Bond Polarity
The polarity of a covalent bond is determined by the difference in electronegativity between the two atoms involved. Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons.
The greater the difference in electronegativity, the more polar the bond will be. For example, the bond between hydrogen and chlorine in hydrogen chloride is highly polar because chlorine is much more electronegative than hydrogen.
Molecule Identification, Which molecule listed below has a polar covalent bond
| Molecule | Chemical Formula | Electronegativity Difference | Bond Polarity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water | H2O | 1.2 | Polar |
| Ammonia | NH3 | 1.0 | Polar |
| Hydrogen chloride | HCl | 1.7 | Polar |
Bond Polarity and Molecular Shape
The polarity of covalent bonds can affect the overall shape of a molecule. Polar covalent bonds can create a dipole moment, which is a measure of the polarity of a molecule.
The dipole moment of a molecule can cause it to align with other molecules, which can affect the physical properties of the substance.
Polarity and Intermolecular Forces
Bond polarity can also contribute to intermolecular forces. Polar covalent bonds can create dipole-dipole interactions, which are attractive forces between polar molecules.
Dipole-dipole interactions can affect the boiling point, melting point, and solubility of a substance.
Questions and Answers: Which Molecule Listed Below Has A Polar Covalent Bond
What is a polar covalent bond?
A polar covalent bond is a type of chemical bond in which the electrons are not shared equally between the atoms involved. This results in a partial positive charge on one atom and a partial negative charge on the other.
What factors influence bond polarity?
The electronegativity difference between the atoms involved is the primary factor that influences bond polarity. Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons. The greater the electronegativity difference, the more polar the bond.
How does bond polarity affect molecular shape?
Bond polarity can affect molecular shape by causing the molecule to adopt a specific geometry that minimizes the repulsion between the partial charges.