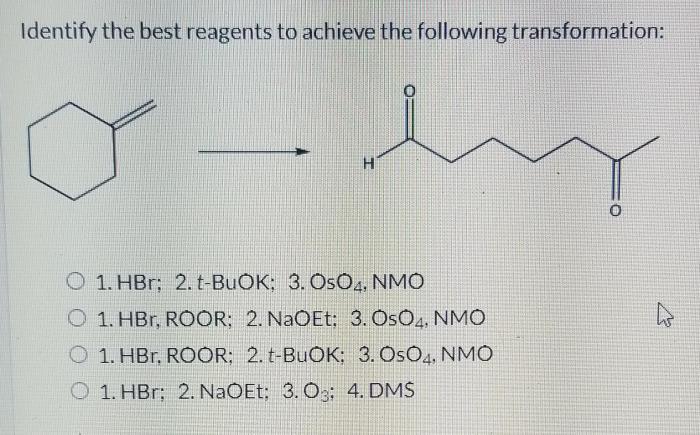
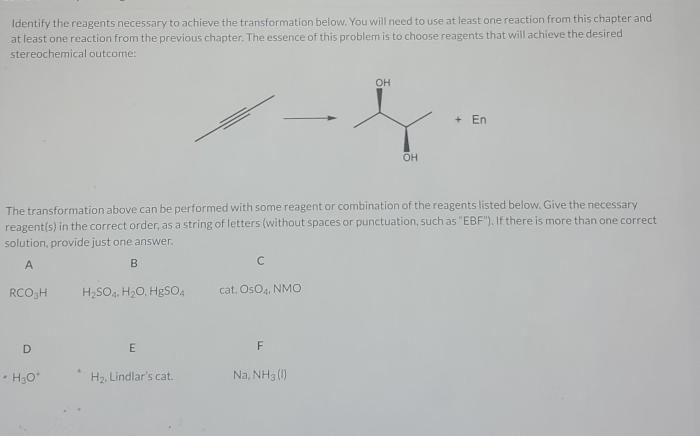
Identify the best reagents to complete the following reaction – In the realm of chemical synthesis, the identification of the most suitable reagents for a given reaction is paramount. This article embarks on an in-depth exploration of the strategies employed to select the ideal reagents, delving into the intricacies of functional group compatibility, reaction mechanisms, reagent reactivity, reaction conditions, and economic considerations.
By unraveling the intricate interplay between these factors, we empower chemists with the knowledge and tools necessary to optimize their synthetic endeavors, leading to the efficient and effective construction of complex molecules.
Identify Suitable Reagents: Identify The Best Reagents To Complete The Following Reaction

Selecting appropriate reagents for a given reaction is crucial to achieving optimal outcomes. Factors to consider include functional group compatibility, reaction mechanism, reagent reactivity, and reaction conditions.
Functional group compatibility refers to the ability of a reagent to react selectively with a specific functional group without affecting other functional groups present in the molecule. For example, alcohols can be oxidized by reagents such as chromic acid or potassium permanganate, while alkenes can be hydrogenated using reagents like hydrogen gas and a metal catalyst.
Explore Reaction Mechanisms
Understanding the reaction mechanism can guide reagent selection. The mechanism reveals the sequence of steps involved in the reaction, including the formation of intermediates and the breaking and formation of bonds. By analyzing the mechanism, one can identify the key functional groups involved and the type of reagent that can facilitate the desired transformation.
For instance, in a nucleophilic substitution reaction, a nucleophile attacks an electrophile, resulting in the substitution of a leaving group. Reagents like sodium hydroxide or potassium tert-butoxide are commonly used as nucleophiles.
Evaluate Reagent Reactivity, Identify the best reagents to complete the following reaction
The reactivity of reagents varies significantly. Factors such as temperature, solvent, and concentration can influence reactivity. A table comparing the reactivity of different reagents for a specific reaction can be helpful in selecting the most suitable one.
For example, in a Diels-Alder reaction, the reactivity of the dienophile is influenced by its electron deficiency. More electron-deficient dienophiles, such as maleic anhydride, react more readily with dienes than less electron-deficient ones.
Consider Reaction Conditions
Reaction conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and solvent, can significantly impact reagent selection and reaction efficiency. For instance, in a Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction, the use of a Lewis acid catalyst, such as aluminum chloride, is essential to activate the electrophile (acyl chloride) and promote the reaction.
By optimizing reaction conditions, one can enhance reagent performance and improve the yield of the desired product.
Assess Reagent Availability and Cost
The availability and cost of reagents are practical considerations. Balancing reagent effectiveness with economic factors is important. Researchers often seek cost-effective alternatives to expensive reagents without compromising reaction outcomes.
For example, in a Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction, the use of inexpensive boronic acids as nucleophiles instead of more expensive organometallic reagents can reduce the overall cost of the reaction.
FAQ Section
What are the key factors to consider when selecting reagents for a chemical reaction?
Functional group compatibility, reaction mechanism, reagent reactivity, reaction conditions, and economic considerations are the primary factors that guide reagent selection.
How does functional group compatibility influence reagent selection?
Functional groups dictate the reactivity of molecules. Selecting reagents that are compatible with the target functional groups ensures efficient reactions and minimizes side reactions.
What is the role of reaction mechanisms in reagent selection?
Understanding the reaction mechanism reveals the intermediate species and transition states involved. This knowledge helps identify reagents that facilitate the desired reaction pathway.